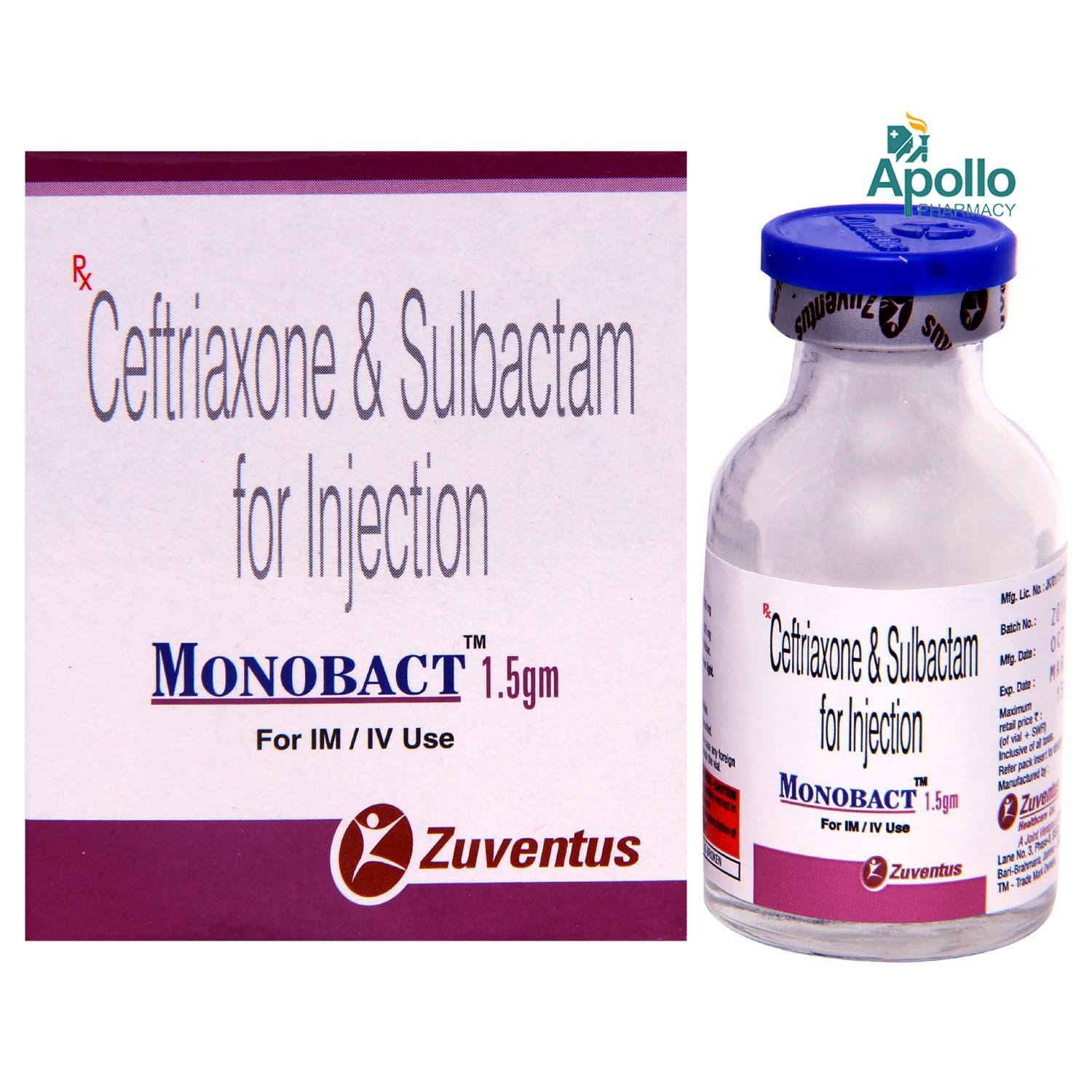
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection 1's


MRP ₹171
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹25.6 Cashback (15%)
Provide Delivery Location
Online payment accepted
 Prescription drug
Prescription drugWhats That
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Return Policy :
Expires on or after :
NPPA :
About Monobact 1.5 gm Injection
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection belongs to the class of medications called ‘antibiotics’ used to treat bacterial infections. Bacterial infections are caused by the multiplication of harmful bacteria inside or on the body. These harmful bacteria produce chemicals known as toxins, which can damage tissue and make you sick. Symptoms of bacterial infection vary depending on the organ affected by bacteria.
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection is a combination of two medicines: Ceftriaxone and Sulbactam. Ceftriaxone is a cephalosporin antibiotic. It has bactericidal action (kills bacteria). It works by preventing the formation of the cell wall (the outer protective layer of bacteria, which is essential for its survival) by preventing protein synthesis. Sulbactam inhibits the action of beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase is an enzyme produced by bacteria that can destroy antibiotics (ceftriaxone).
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection will be administered by a healthcare professional, so do not self-administer. The common side effects of Monobact 1.5 gm Injection include pain and swelling at the injection site, skin rash, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and black/tarry stools. These side effects are usually mild and temporary. However, if these side effects persist or worsen, inform your doctor immediately.
It is not recommended to take Monobact 1.5 gm Injection if you are allergic to penicillin or any cephalosporin antibiotic or its contents. Before taking Monobact 1.5 gm Injection, inform your doctor if you have kidney problems, liver disease, diabetes or using other antibiotics. Do not discontinue or abruptly stop using Monobact 1.5 gm Injection as it may lead to antibiotic resistance (bacteria become resistant to antibiotics). Before taking Monobact 1.5 gm Injection, inform your doctor if you have an electrolyte imbalance, seizures, or gastrointestinal diseases. Monobact 1.5 gm Injection is probably safe when used in children, pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers and the elderly. Monobact 1.5 gm Injection may not interact with alcohol. Monobact 1.5 gm Injection may cause dizziness, so do not drive or operate heavy machinery if you feel dizzy.
Uses of Monobact 1.5 gm Injection
Directions for Use
Medicinal Benefits
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection contains Ceftriaxone and Sulbactam. Ceftriaxone is a cephalosporin antibiotic, whereas Sulbactam is a beta-lactamase inhibitor. Monobact 1.5 gm Injection has broad-spectrum activity and is effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It makes the drug effective in multiple serious bacterial infections, including infections of the bloodstream (septicemia), bones (osteomyelitis), the heart valves (endocarditis), the membranes protecting the brain (meningitis), acute bacterial otitis media (infection of the middle ear) and the lining of the abdomen (peritonitis) and to prevent and treat infections following surgeries.
Storage
- Apply a hot/cold pack to the affected area.
- Doing gentle exercises can help cope with pain by stretching muscles.
- Get enough sleep. It helps enhance mood and lower pain sensitivity.
- Avoid alcohol, smoking and tobacco as they can increase pain.
- Follow a well-balanced meal.
- Meditation and massages may also help with pain.
- Rash caused by allergies is due to irritants or allergens. Therefore, avoid contact with such irritants.
- Consult your doctor for proper medication and apply an anti-itch medication. Follow the schedule and use the medication whenever needed.
- Protect your skin from extreme heat and try to apply wet compresses.
- Soak in the cool bath, which gives a soothing impact to the affected area.
- Eosinophil levels can be lowered by eating fruits and vegetables, avoiding smoking, and consuming alcohol in moderation.
- Several foods, such as ginger, garlic, pepper, turmeric, and honey, might boost immunity.
- Avoid dairy products, including cheese, yoghurt, and milk.
- Drink water and keep yourself hydrated.
Drug Warnings
It is not recommended to take Monobact 1.5 gm Injection if you are allergic to penicillin, any cephalosporin antibiotic, or its contents. Before taking Monobact 1.5 gm Injection, inform your doctor if you have kidney problems, liver disease, diabetes or using other antibiotics. Do not discontinue or abruptly stop using Monobact 1.5 gm Injection as it may lead to antibiotic resistance (bacteria become resistant to antibiotics). Before taking Monobact 1.5 gm Injection, inform your doctor if you have an electrolyte imbalance, seizures, or gastrointestinal diseases. Monobact 1.5 gm Injection is probably safe when used in children, pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers and the elderly. Monobact 1.5 gm Injection may not interact with alcohol. Monobact 1.5 gm Injection may cause dizziness, so do not drive or operate heavy machinery if you feel dizzy. Alterations in prothrombin time (a test used to check for bleeding problems) have been reported in patients receiving this medicine. Antibiotic therapy will cause an imbalance in the normal microbial flora of the large intestine, which may promote the growth of a bacteria called Clostridium difficile, and you may experience severe diarrhoea.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Co-administration of Calcium chloride with Monobact 1.5 gm Injection can increase the risk of side effects.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Monobact 1.5 gm Injection with Calcium chloride is not recommended, but can be taken together if prescribed by a doctor. However, consult your doctor if you experience any unusual symptoms contact your doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Co-administration of Calcium gluconate with Monobact 1.5 gm Injection can increase the risk of adverse effects.
How to manage the interaction:
Taking Monobact 1.5 gm Injection with Calcium gluconate is not recommended, but can be taken together if prescribed by a doctor. However, consult your doctor if you experience any unusual symptoms contact a doctor immediately. Do not discontinue any medications without consulting a doctor.
Taking the cholera vaccine after or along with Monobact 1.5 gm Injection may reduce the activity of the vaccine.
How to manage the interaction:
Although taking Monobact 1.5 gm Injection and Cholera, live attenuated together can evidently cause an interaction, it can be taken if your doctor has suggested it. To ensure adequate vaccine response, you should not receive cholera vaccine, live until at least 14 days after you complete your antibiotic therapy. In case you experience any unusual side effects, consult a doctor. Do not stop using any medications without a doctor's advice.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Probiotics should be taken after taking the full course of Monobact 1.5 gm Injection to restore some healthy bacteria in the intestines that may have been killed. Taking probiotics after antibiotic treatment can reduce the risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Certain fermented foods like yogurt, cheese, sauerkraut, kombucha and kimchi can help restore the intestine's good bacteria.
- Include more fibre-enriched food in your diet, as it can be easily digested by gut bacteria, which helps stimulate their growth. Thus, fibre-rich foods may help restore healthy gut bacteria after antibiotics. Whole grains like whole-grain bread and brown rice should be included in your diet.
- Avoid alcoholic beverages with Monobact 1.5 gm Injection as they can make you dehydrated and may affect your sleep. This can make it harder for your body to aid the Monobact 1.5 gm Injection in fighting off infections.
Side Effects of Monobact 1.5 gm Injection
- Pain at the injection site
- Swelling at the injection site
- Skin rash
- Diarrhoea
- Anaphylaxis
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Black/tarry stools
Habit Forming
Therapeutic Class
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Out of StockNot for online saleActocef-S 1000mg/500mg Powder for Injection
Fitwel Pharmaceuticals
₹103.62
(₹93.26 per unit)
39% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockNot for online saleAdvotrax S 1000mg/500mg Injection
₹115
(₹103.5 per unit)
32% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockNot for online saleAcocef-SB Injection
₹123
(₹110.7 per unit)
28% CHEAPER
Product Substitutes
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
FAQs
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection is used to treat bacterial infections. It contains Ceftriaxone and Sulbactam. Ceftriaxone reduces the infection by inhibiting bacterial growth. It disrupts the formation of the cell wall (outer layer), which is essential for bacteria's survival. Sulbactam inhibits the action of beta-lactamase, an enzyme bacteria produce to destroy antibiotics. Sulbactam enhances the activity of ceftriaxone.
Common side effects of Monobact 1.5 gm Injection are pain and swelling at the injection site, skin rash, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and black/tarry stools. These side effects are usually mild and temporary. However, if any of these side effects persist or worsen, inform your doctor immediately.
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection should be avoided in conditions like gastrointestinal diseases, liver diseases, kidney diseases, seizure disorders, bleeding disorders, antibiotic resistance and bleeding disorders.
Do not stop taking Monobact 1.5 gm Injection suddenly because your symptoms may improve before the infection is completely cured. Complete the full course of treatment even if you feel better.
People allergic to penicillin should not take Monobact 1.5 gm Injection as they may develop cross-sensitivity (sensitivity to drugs with similar structures). Monobact 1.5 gm Injection contains ceftriaxone, which has a similar structure to that of penicillin.
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- CHOLERA VACCINE
- ETHINYLESTRADIOL
- MEZLOCILLIN
- AZLOCILLIN
- AMIKACIN
- STREPTOMYCIN
- NEOMYCIN
- GENTAMICIN
- CYCLOSPORINE
- PROBENECID
Special Advise
- Inform your doctor if you are allergic to penicillin or other antibiotics.
- Take it with food and plenty of fluids to avoid an upset stomach.
Disease/Condition Glossary
Bacterial infections: A bacterial infection occurs when dangerous bacteria enter the body, flourish, and spread throughout it. It multiplies quickly and can attack any organ in the body. A lot of them emit toxins, which can harm the tissue and make you ill. Minor illnesses like sore throats and ear infections to serious brain infections are all caused by bacteria (like meningitis and encephalitis). Generalized symptoms like fevers, chills, and fatigue can occur when you become infected with bacteria. Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and E. coli are a few harmful bacteria that frequently cause infections. Anyone can contract a bacterial infection, but those with weakened immune systems or those taking immunosuppressive drugs like steroids are more vulnerable.

Have a query?
Buy best Infections & Infestation products by
Cipla Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
FDC Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Biochem Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
United Biotech Pvt Ltd
Hetero Drugs Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Fusion Health Care Pvt Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
Zydus Cadila
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Converge Biotech Pvt Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Hetero Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
AAA Pharma Trade Pvt Ltd
Gufic Bioscience Ltd
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Wallace Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Medishri Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Hegde & Hegde Pharmaceutica Llp
Veritaz Healthcare Ltd
Ranbaxy Laboratories Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Shreya Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Overseas Health Care Pvt Ltd
Biocon Ltd
Indchemie Health Specialities Pvt Ltd
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Brinton Pharmaceuticals Ltd
J B Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Unifaith Biotech Pvt Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Biochemix Health Care Pvt Ltd
Natco Pharma Ltd
Samarth Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Unichem International
Laborate Pharmaceuticals India Ltd
Unipark Biotech Pvt Ltd
Zymes Bioscience Pvt Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Neon Laboratories Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
DR Johns Lab Pharma Pvt Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Medgen Drugs And Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Novartis India Ltd
Canixa Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Icarus Health Care Pvt Ltd
Lincoln Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Celon Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Concept Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Klm Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Nicholas Piramal India Ltd
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Yuventis Pharmaceuticals
Capital Pharma
German Remedies Ltd
Pristine Pearl Pharma Pvt Ltd
Unison Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Aurz Pharmaceutical Pvt Ltd
Clover Health Care Pharma
Kepler Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Allites Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Auspharma Pvt Ltd
Intra Life Pvt Ltd
Jolly Healthcare
Linux Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Ozone Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cachet Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Comed Chemicals Ltd
Delcure Life Sciences Ltd
Fresenius Kabi India Pvt Ltd
Khandelwal Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Alcohol
Caution
It is advisable to avoid alcohol consumption to prevent unintended side effects.
Pregnancy
Caution
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection is not recommended for use in pregnancy unless absolutely necessary. Inform your doctor if you are pregnant. Your doctor may prescribe this medicine if the benefits outweigh the risks.
Breast Feeding
Caution
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection is not recommended for use in breastfeeding unless absolutely necessary. Inform your doctor if you are breastfeeding. Your doctor may prescribe this medicine if the benefits outweigh the risks.
Driving
Caution
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection may decrease your alertness and vision or make you sleepy and dizzy. Do not drive if these symptoms occur after receiving this medicine.
Liver
Caution
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection should be used with caution if you have liver function impairment due to the increased risk of worsening your condition. Regular monitoring of liver function tests, appropriate dose adjustments or replacement with a suitable alternative medicine may be required in some cases based on your clinical condition.
Kidney
Caution
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection should be used with caution if you have a history of renal function impairment due to the increased risk of severe side effects. Close monitoring of kidney function, appropriate dose adjustments or replacement with alternative medicine may be required in some cases based on your clinical condition.
Children
Caution
Monobact 1.5 gm Injection is probably safe when used in children. However, your doctor may adjust the dose based on age, body weight and health condition of your child.