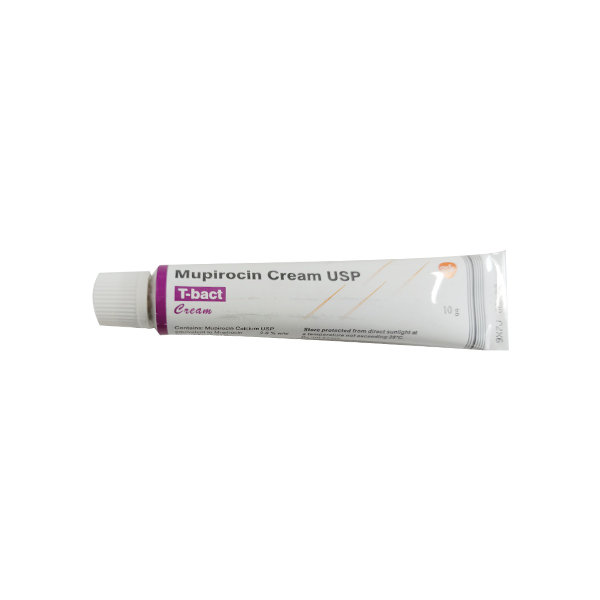
Mupitret Cream 10 gm






MRP ₹230
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹34.5 Cashback (15%)
Provide Delivery Location
Online payment accepted
 Prescription drug
Prescription drugWhats That
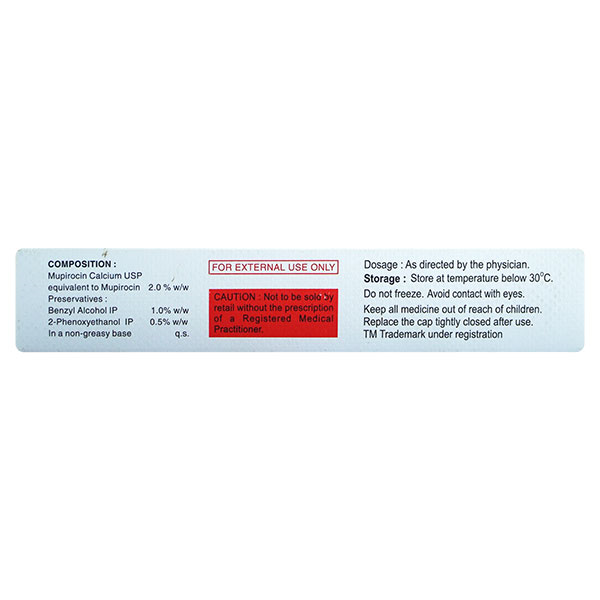
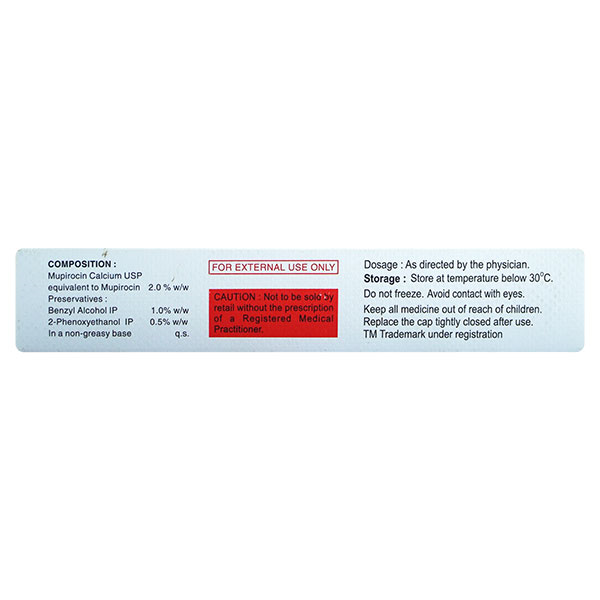
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :
About Mupitret 2%W/W Cream
Mupitret 2%W/W Cream is a novel topical antibiotic used to treat skin infection 'impetigo' caused by bacterias namely Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. A bacterial infection is a condition in which bacteria grows in the body and cause infection. It can target any body part and multiple very quickly.
Mupitret 2%W/W Cream works by stopping the production of necessary proteins needed for bacterial surveillance. It is also active against Gram-negative organisms such as Escherichia coli and Haemophilus influenza. It is not effective against fungal or viral infections, and should not be applied on burnt skin areas and open-cut wound.
Mupitret 2%W/W Cream should only be used if advised by your doctor. It is not recommended for children below 2 months of age. Mupitret 2%W/W Cream should be used for skin only and accidentally if it gets into your eye, mouth or nose rinse with water. Mupitret 2%W/W Cream should be applied to the affected area with a piece of clean cotton wool or gauze swab. Mupitret 2%W/W Cream should not be applied more than the recommended dose, to avoid unpleasant side effects. And also, the course should be completed even if you feel better as it is an antibiotic. Some common side effects of Mupitret 2%W/W Cream are burning, itching, redness, stinging and dryness on your skin in the place where Mupitret 2%W/W Cream is applied. Sensitive allergic reaction (skin hypersensitivity reactions) like rashes, itching, swelling, and shortness of breath can occur in rare cases. Please consult your doctor if an allergic reaction becomes severe.
Tell your doctor if you are known to allergic to Mupitret 2%W/W Cream or any other medicines. It is not known whether Mupitret 2%W/W Cream harm baby or passes into breast milk. It is better to contact a doctor before using Mupitret 2%W/W Cream during pregnancy and while breastfeeding. If nursing mothers are applying Mupitret 2%W/W Cream to their breast or nipple, they should wash the affected area thoroughly before nursing their baby.
Uses of Mupitret 2%W/W Cream
Directions for Use
Key Benefits
Mupitret 2%W/W Cream is widely used to treat skin infections due to specific bacteria. This medicine works by killing bacteria or preventing their growth.
Storage
- Hydrate your body: Drink enough water to prevent dehydration and headaches.
- Calm Your Mind: Deep breathing and meditation can help you relax and relieve stress.
- Rest and Recharge: Sleep for 7-8 hours to reduce headache triggers.
- Take rest: lie down in a quiet, dark environment.
- Cold or warm compresses can help reduce tension.
- Stay Upright: Maintain good posture to keep symptoms from getting worse.
- To treat headaches naturally, try acupuncture or massage therapy.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers include acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
- Prescription Assistance: Speak with your doctor about more substantial drug alternatives.
- Severe Headaches: Seek emergency medical assistance for sudden, severe headaches.
- Frequent Headaches: If you get reoccurring headaches, consult your doctor.
- Headaches with Symptoms: Seek medical attention if your headaches include fever, disorientation, or weakness.
- Skin rash caused by allergies is due to irritants or allergens. Therefore, avoid contact with such irritants.
- Consult your doctor for proper medication and apply an anti-itch medication. Follow the schedule and use the medication whenever needed.
- Protect your skin from extreme heat and try to apply wet compresses.
- Soak in the cool bath, which gives a soothing impact to the affected area.
- Inform your doctor about the nausea and discuss possible alternatives to the medication or adjustments to the dosage.
- Divide your daily food intake into smaller, more frequent meals to reduce nausea.
- Opt for bland, easily digestible foods like crackers, toast, plain rice, bananas, and applesauce.
- Avoid certain foods that can trigger nausea, such as fatty, greasy, spicy, and smelly foods.
- Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broth, or electrolyte-rich beverages like coconut water or sports drinks.
- Use ginger (tea, ale, or candies) to help relieve nausea.
- Get adequate rest and also avoid strenuous activities that can worsen nausea.
- Talk to your doctor about taking anti-nausea medication if your nausea is severe.
- Record when your nausea occurs, what triggers it, and what provides relief to help you identify patterns and manage your symptoms more effectively.
- Report the itching to your doctor immediately; they may need to change your medication or dosage.
- Use a cool, damp cloth on the itchy area to help soothe and calm the skin, reducing itching and inflammation.
- Keep your skin hydrated and healthy with gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers.
- Try not to scratch, as this can worsen the itching and irritate your skin.
- If your doctor prescribes, you can take oral medications or apply topical creams or ointments to help relieve itching.
- Track your itching symptoms and follow your doctor's guidance to adjust your treatment plan if needed. If the itching persists, consult your doctor for further advice.
- Apply moisturizer immediately after showering or bathing.
- Use a moisturizer containing lanolin, petroleum jelly, glycerine, hyaluronic acid or jojoba oil.
- Do not use hot water for bathing. Instead use warm water and limit showers and bath to 5 to 10 minutes.
- Apply a sunscreen with SPF-30 or higher.
- Avoid harsh soaps, detergents and perfumes.
- Do not scratch or rub the skin.
- Drink adequate water to prevent dehydration.
- Wear pants, full sleeves and a wide-brimmed hat while going out in the sun.
- Consult your doctor if you experience skin redness, itching, or irritation after taking medication.
- Your doctor may adjust your treatment plan by changing your medication or providing guidance on managing your erythema symptoms.
- Your doctor may recommend or prescribe certain medications to help alleviate symptoms.
- Apply cool compresses or calamine lotion to the affected skin area to reduce redness and itching.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water to help alleviate symptoms and keep your skin hydrated.
- Monitor your skin condition closely and promptly report any changes, worsening symptoms, or concerns to your healthcare provider.
- Consult and seek guidance from a doctor or healthcare expert to determine the cause and best course of treatment.
- Avoid harsh products, extreme temperatures, and other potential irritants that may exacerbate the issue.
- Depending on the location and severity of the burning, your healthcare professional may recommend applying a soothing or protective agent, such as a cream, gel, or ointment.
- Keep the affected area clean to promote healing and prevent further irritation.
- Schedule follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional to monitor your symptoms and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
- If the burning or irritation persists or worsens, seek medical attention for further guidance and treatment.
Drug Warnings
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea (CDAD) has been reported while using major topical antibacterial products. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, the ongoing treatment of Mupitret 2%W/W Cream should be discontinued. Mupitret 2%W/W Cream should be stopped if irritation, severe itching, or skin rash occurs. If there is no improvement observed in 3-5 days, contact your doctor. Mupitret 2%W/W Cream should be used with caution in children less than 2 months of age. Prolonged use of Mupitret 2%W/W Cream may result in the overgrowth of fungi. Rinse with water in a case Mupitret 2%W/W Cream accidentally enters your nose, eyes, or mouth. A separate product of nasal is available for use in the nose. Mupitret 2%W/W Cream topical is for use only on the skin. Do not apply on the burnt skin or open cut wound.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Side Effects of Mupitret 2%W/W Cream
- Burning
- Itching
- Redness
- Stinging
- Dryness
Habit Forming
Therapeutic Class
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Mupinext Cream 5 gm
Ethinext Pharma
₹84
(₹15.12/ 1gm)
26% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockMiprosub Cream
₹169
(₹15.21/ 1gm)
26% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockBactrocare Cream 5 gm
Tergum Remedies Pvt Ltd
₹85
(₹15.3/ 1gm)
26% CHEAPER
Product Substitutes
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Drug-Diseases Interactions
Login/Sign Up
FAQs
Your symptoms may improve before the infection is completely cured. But, it would be suggested to complete the full course of treatment even if you feel better.
Exercise caution while using this medicine for treating skin with any open wounds unless suggested by your doctor. Not be used around eyes or nose.
Apply a small amount of Mupitret 2%W/W Cream, with a cotton swab or gauze pad to the affected area of the skin as per the dosage and schedule prescribed by your doctor
Apply the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next dose. Do not use extra medicine to make up for the missed dose.
Antibiotic medicines can cause diarrhoea, which may be a sign of a new infection. If you have diarrhoea that is watery or bloody, call your doctor. Do not use anti-diarrheal medicine unless your doctor tells you to.
Disease/Condition Glossary
Your skin is your body’s largest organ. Its aim is to protect your body against infection. The skin itself gets infected occasionally. Infections of bacterial skin frequently begin as tiny, red bumps that increase in size slowly. A wide variety of germs cause skin infections, and symptoms can range from mild to severe. With over-the-counter medications and home remedies, mild infections may be treatable, while other infections may need medical attention.

Have a query?
Buy best Dermatology products by
Others
AYUR
FIXDERMA
BIODERMA
VENUSIA
CANDID
SELSUN
ABZORB
ATODERM
CIPHANDS
KETO
MINTOP
UVAVO
8X
MELALUMIN
MORR
OILATUM
REJUHAIR
SUNCROS
TETMOSOL
UNISON
UV DOUX
ATBRO SAFEXX
BETADINE
COLOPLAST
DR. MOREPEN
HAIR 4U
LA SCREEN
MEDERMA
RING GUARD
SHYN-ON
SOLSET
SUNSTOP
YUVINIE
A-DERMA
AHD
ALCONANZ
AQUAHOLD
AVARTA
AVENE
BIOLINE
BIOWRIGHT
CETRILAK
CUTICOLOR
CUTILOCK
DANDEL PLUS
DEOPHIN
DOUX
DYSIS
ENMASK 50
EXIZOL
FAIR INSTA
GETRYL
GORGEUS
GUNEERA
HAIR YUTH
HH MITE
I-GLOW
ITCH GUARD
KETOFLY
KETOMAC
KETOPZ
KETOSTAR
KZ
LIPZ
MANKIND
MEDRAYS
MELAGARD
MELNORA BLUV
MICROSTERILE
NO SCARS
OAKNET
ONABET
PARASOFT
PERCOS
PHOTON
PHOTOSTABLE
PHYSIOGEL
PROTEK
RADIBAN
RASHFREE
REGALIZ
RENOCIA
SALISIA
SEBANDRO
SEBORBAR
SESTRY
SOLASAFE
SOLECROSS
STERILLIUM
SUDERMA
SUN KROMA
SUNCLIP
SUNHEAL
SUNMATE
SUNTRIS
TAIYU
TEDIBAR
THERUPTOR
TRICOGRO
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Klm Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Cipla Ltd
Canixa Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Atopic laboratories Pvt Ltd
Hegde & Hegde Pharmaceutica Llp
Brinton Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Amwill Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Palsons Derma Pvt Ltd
Oaknet Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Med Manor Organics Pvt Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Dermocare Laboratories Gujarat Llp
Fixderma India Pvt Ltd
Apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Yaher Pharma
Systopic Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Menarini India Pvt Ltd
Ethinext Pharma
Nemus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Skinocean Pharmaceuticals
Dermacia Healthcare
Inex Medicaments Pvt Ltd
Lupin Ltd
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Talent India Pvt Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Kivi Labs Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
Hbc Dermiza Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Mrhm Pharma Pvt Ltd
Regaliz Medicare Ltd
Sol Derma Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Newtrimed Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Wallace Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Eskon Pharma
Glowderma Lab Pvt Ltd
La Pristine Bioceuticals Pvt Ltd
Mohrish Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Percos India Pvt Ltd
Rockmed Pharma Pvt Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Praise Pharma
Ethicare Remedies Pvt Ltd
Kaizen Drugs Pvt Ltd
Aurel Biolife
Rely On Pharmaceuticals
Wockhardt Ltd
Galcare Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
La Med Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Biocute Life Care
Yap Bioceuticals
Yash Pharma Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Zee Laboratories Ltd
Apple Therapeutics Pvt Ltd
Adonis Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Albatross Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Galderma India Pvt Ltd
Prism Life Sciences Ltd
FDC Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Salve Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
West Coast Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Dermarex HealthCare India Pvt Ltd
Arka Vital Science Pvt Ltd
Dermajoint India
Gary Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Grace Derma Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Karlin Pharmaceuticals & Exports Pvt Ltd
Skinska Pharmaceutica Pvt Ltd
Uniza Healthcare Llp
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cosmofix Technovation Pvt Ltd
Human Pharmaceuticals
Indolands Pharma Pvt Ltd
Lyra Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Entod Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Iceberg Health Care Pvt Ltd
Jenburkt Pharmaceuticals Ltd
P and P Dermaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Dabur India Ltd
Indchemie Health Specialities Pvt Ltd
Olcare Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Unison Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
BODY CREAM
Body Lotion
Face Cream
Shampoo
Sun Screen
Face Gel
Soap
Face Wash
HAIR SOLUTION
Face Serum
BODY GEL
Hair Lotion
Hair Serum
Dusting Powder
ANTISEPTIC
FACE CLEANSER
Face Lotion
Body Wash
Body Spray
Eye Cream
FUNGAL INFECTION
Foot Cream
Conditioner
Eye Gel
Cleanser
Hair Cream
Hair Oil
Face Mask
Hair Gel
Sanitizer
Hair Spray
Moisturiser
Skin Ointment
Lip Balm
Capsule
Eye Serum
Intimate Wash
Specialty Supplements
Hand Cream
Facial Spray
SPECIALITY SUPPLEMENT
Face Toner
MEDICATED SHAMPOO
Tablet
Talcum Powder
BABY SUNSCREEN
Body Butter
Body Scrub
DIAPER RASH CREAM
EYE SOLUTION
FACIAL WIPE
Gargle
Hand Wash
Intimate Spray
Lip Serum
Lubricant Gel
MEDICATED CREAM
Nail Polish
VITAMIN D
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
No reported interaction with Mupitret 2%W/W Cream. But, It is best to avoid alcohol while taking medication.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Mupitret 2%W/W Cream is a category B pregnancy drug. Limited human data suggests that the drug does not represent any significant risk to the baby.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
It is not known whether Mupitret 2%W/W Cream harm baby or passes into breast milk in the breastfeeding state. So, it is better to contact a doctor before using Mupitret 2%W/W Cream during breastfeeding. If nursing mothers are applying Mupitret 2%W/W Cream to their breast or nipple, they should wash the affected area thoroughly before nursing their baby.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Mupitret 2%W/W Cream has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive or use machines.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Mupitret 2%W/W Cream does not have any reported interaction hence, in case you experience any difficulty discuss with your doctor.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Mupitret 2%W/W Cream does not have any reported interaction hence, in case you experience any difficulty discuss with your doctor.
Children
Safe if prescribed
Mupitret 2%W/W Cream can be given safely to children provided; dose has been prescribed by a child specialist. However, Mupitret 2%W/W Cream should not be used in children less than 2 months of age.