Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops
MRP ₹60
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹9.0 Cashback (15%)
Provide Delivery Location
Online payment accepted
 Prescription drug
Prescription drugWhats That
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :
About Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops
Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops is a combination of corticosteroid and an antibiotic that treats bacterial infections of the eye and ear. Bacterial infection occurs when bacteria invade and multiply in the body.
Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops contains Dexamethasone and Ofloxacin. Dexamethasone belongs to the class of corticosteroids. It blocks the production of prostaglandins (chemical messengers) that make the affected area red, swollen, and itchy. Ofloxacin belongs to a class of drugs called quinolone antibiotics. It is bactericidal (kills bacteria) and works by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase, an enzyme required for the replication, transcription, and repair of the DNA.
Your doctor will advise the appropriate dose that suits your infection. Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops is for external use only. Common side effects of Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops when used as eye drops include irritation, itching, redness, burning or a stinging sensation, and temporary blurred vision. The side effects of ear drops include mild irritation, ear discomfort, headache, earache, taste changes, and dizziness. Most of these side effects do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. If these side effects persist longer, please consult your doctor.
Let your doctor know if you are sensitive to Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops or any other medications. Please inform your doctor if you have frequent ear infections, perforated ear drum, recent eye surgery, cataracts, glaucoma, severe nearsightedness, or diabetes before using Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops. Pregnant and breastfeeding mothers should consult the doctor before starting Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops. This medicine may cause temporary blurred vision; hence drive only when alert. Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops should be used for children only when advised by a doctor.
Uses of Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops
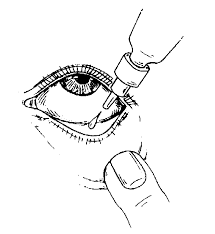
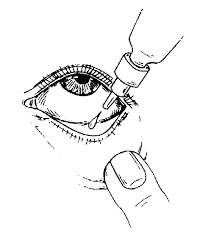
Directions for Use
Key Benefits
Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops contains Dexamethasone and Ofloxacin. Dexamethasone is a corticosteroid and blocks prostaglandins' production (chemical messengers) that make the affected area red, swollen and itchy. Ofloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic that inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase, an enzyme required for DNA replication, transcription, and repair. Thus Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops treats bacterial eye and ear infections.
Storage
Drug Warnings
Before using Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops, let your doctor know if you have a history of eye problems (glaucoma and cataract), heart, liver or kidney diseases, frequent ear infections, perforated ear drum, recent eye surgery, severe nearsightedness, and diabetes. Avoid touching the dropper with bare hands while administering drops since it contaminates the dropper tip and solution. It is advised to check with your doctor before using Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Avoid driving or operating machines since the administration of eye drops may cause blurred vision for a while after use. Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops should be used for children only when advised by a doctor.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Manage stress, eat healthily, drink plenty of water, exercise regularly, and get plenty of sleep.
- Eat food rich in antioxidants such as berries, spinach, kidney beans, dark chocolate, etc.
- Know your allergy triggers, such as pollen, dust and other factors.
- Avoid getting things like shampoo, soap, and water into the ear, as it can cause itching.
- Do not poke or scratch the ear, as it can cause damage to the ear canal, leading to inflammation. The inflamed skin can be infected by bacteria or fungi, which can cause infections in the ear.
- Do not rub your eyes even though some ophthalmic drugs make your eye itchy.
- If you wear contact lenses: Clean and replace contact lenses more often. Never share contact lenses. Always remember to wash your hands before inserting and after removing the contact lens.
- Avoid staring at digital screens for longer durations. Rest your eyes every 20 minutes.
- Avoid or limit the intake of alcohol and caffeine.
Side Effects of Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops
Eye drops:
- Irritation
- Itching
- Redness
- Burning or a stinging sensation
- Temporary blurred vision
Ear drops:
- Mild irritation
- Ear discomfort
- Headache
- Earache
- Taste changes
- Dizziness
Habit Forming
Therapeutic Class
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
FAQs
Special Advise
It is advised to contact your doctor if the infection symptoms persist or worsen after two weeks of treatment.
Disease/Condition Glossary
Bacterial eye infection: A bacterial eye infection occurs when bacteria invade any part of the eyeball or its surrounding tissues, including the cornea (clear front surface of the eye) and the conjunctiva (thin membrane lining the outer eye and inner eyelids). A bacterial eye infection symptoms include red eyes, pain, swelling of the eyes, watery eyes, itching, and blurry vision. Some very common eye infections are conjunctivitis (the inflammation and irritation of the eye's mucous membrane (conjunctiva), stye (bump on the eyelid), uveitis inflammation of the uvea (middle layer of the eye), marginal keratitis (inflammation of the cornea), and blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids).
Bacterial ear infection: Bacterial ear infection occurs when bacteria infect the outer or middle ear. The most common bacterial strains that cause ear infections are Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenza. Symptoms include earache (sharp, sudden pain or a dull, continuous pain), a feeling of fullness in the ear, ear drainage, and muffled hearing. Treatment may include over-the-counter painkillers, anti-allergic drugs, antibiotics, and steroids.

Have a query?
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
It is not known whether alcohol interacts with Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops. Hence, it is advised to limit alcohol consumption while you are being treated with Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Limited information is available on the use of Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops in pregnancy. If you are pregnant, please consult your doctor before using Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
If you are breastfeeding, please consult your doctor before using Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops may cause side effects like blurred vision or dizziness, affecting your driving ability. Do not drive or operate machinery in such cases. Drive only when you are alert and have clear vision.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Let your doctor know if you have any history of liver diseases before taking Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Let your doctor know if you have any history of kidney diseases before taking Ofax-D 10Ml Eye/Ear Drops.
Children
Safe if prescribed
Please consult your doctor. Your doctor will prescribe this medicine based on the condition of your child.