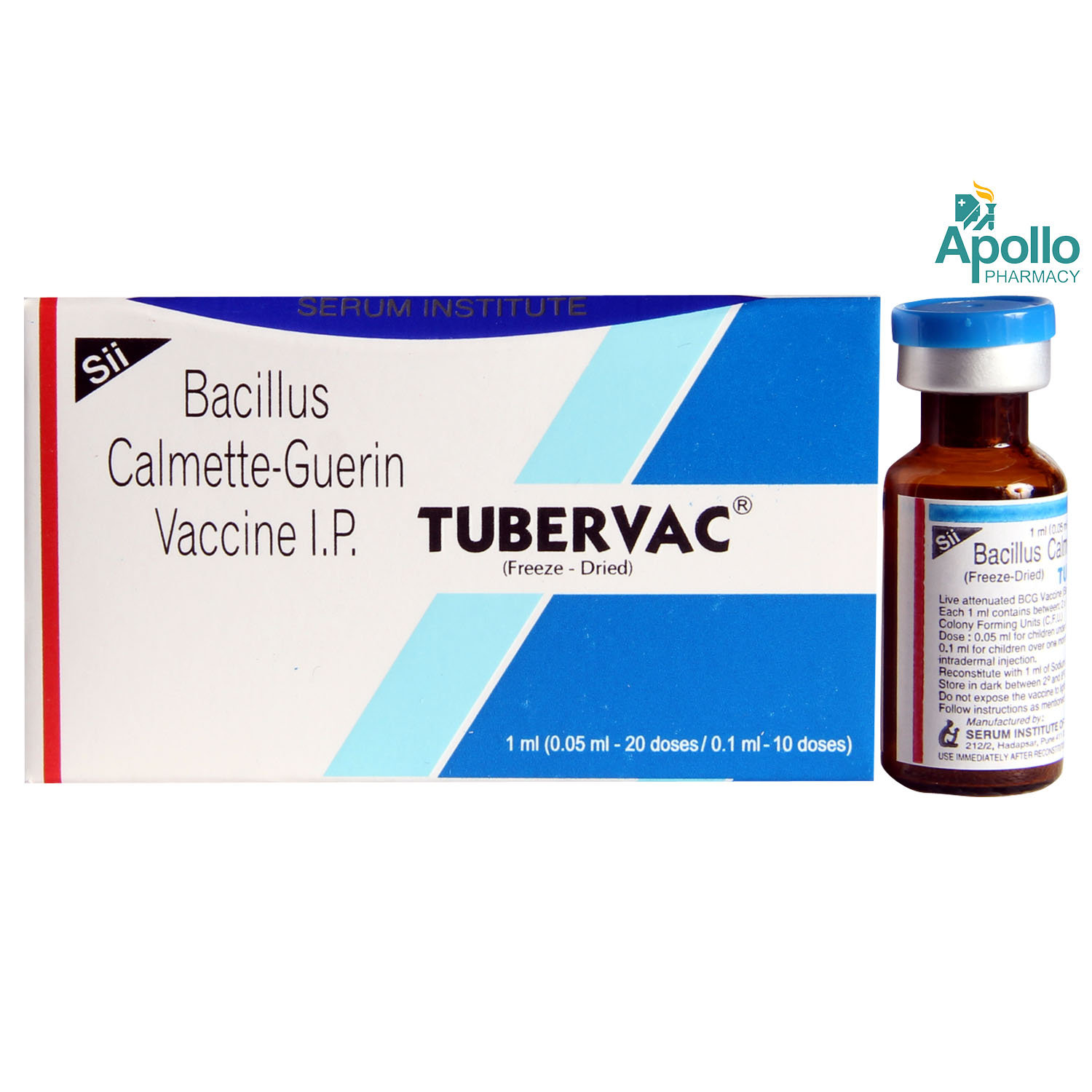
Tubervac Injection 1ml
MRP ₹116.5
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹14.0 Cashback (12%)
Extra 10% Off with Bank Offers
Provide Delivery Location
Non returnable*
COD available
Online payment accepted
 Prescription drug
Prescription drugWhats That
Composition :
BACILLUS CALMETTE GUERIN
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Serum Institute Of India Pvt Ltd
Consume Type :
Parenteral
Expires on or after :
Return Policy :
Not Returnable
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
FAQs

Have a query?
Buy Now
Add to Cart