Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's
MRP ₹136
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹20.4 Cashback (15%)
Provide Delivery Location
Online payment accepted
 Prescription drug
Prescription drugWhats That
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Return Policy :
About Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's
Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's belongs to the Vitamins class, primarily used to treat nutritional deficiencies. Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's effectively treats various conditions caused due to lack of vitamins, such as folate, vitamin B1, B6, and B12 deficiencies. Nutritional deficiency occurs when the body cannot absorb or get enough nutrients from food.
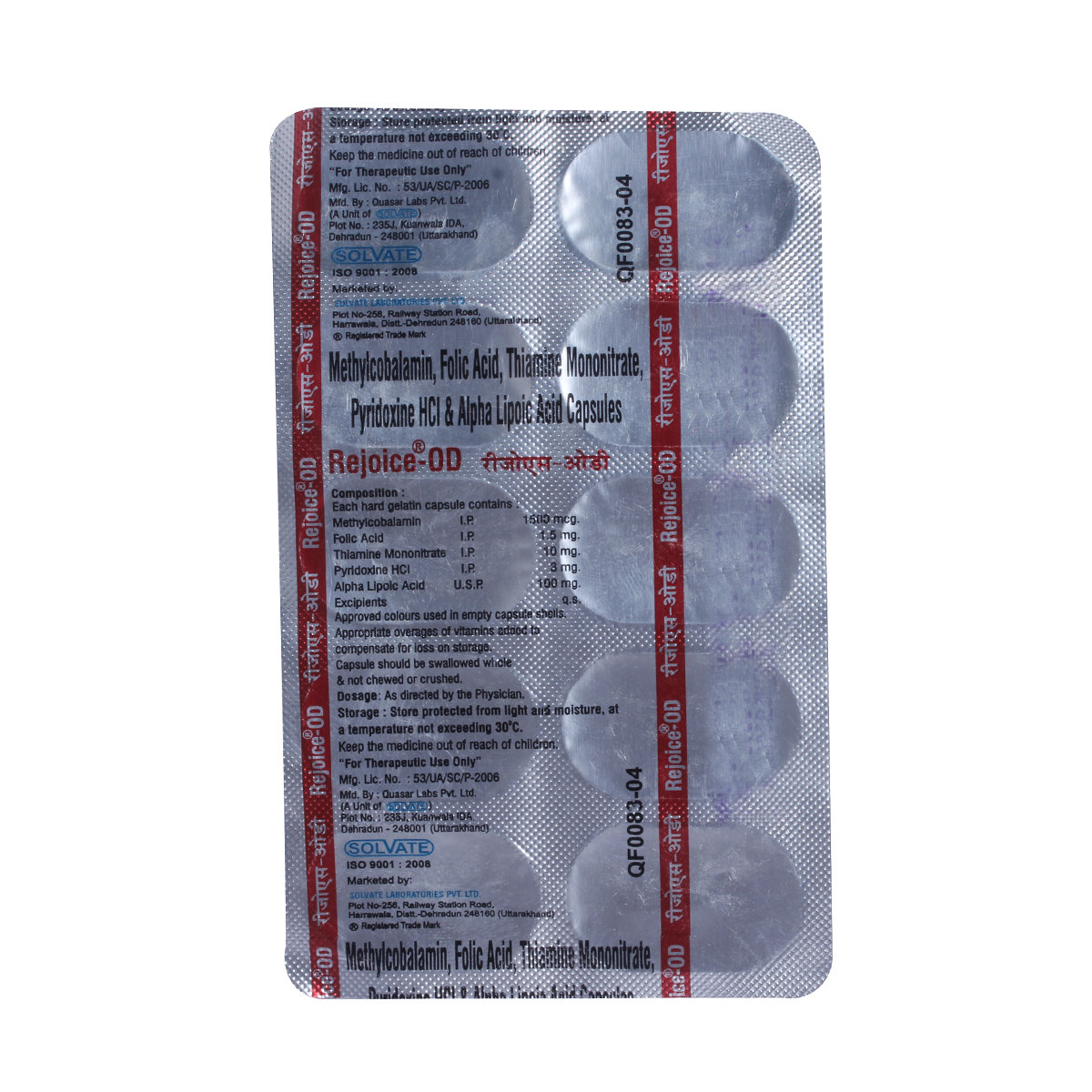
Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's contains Alpha lipoic acid, Folic acid, Pyridoxine, Thiamine, and Mecobalamin. Alpha-lipoic acid is an antioxidant that prevents cell damage and restores vitamin levels in the body. Folic acid is the synthetic form of folate; it helps in the formation of red blood cells and prevents DNA changes that may lead to cancer. Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) is a water-soluble vitamin that regulates body functions, such as cell multiplication, blood formation, and protein synthesis. Thiamine (vitamin B1) helps generate energy from nutrients and aids in the growth and development of body cells. Mecobalamin, a form of vitamin B12, regulates body functions such as cell multiplication, blood formation, and protein synthesis. Together, Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's effectively treats nutritional deficiencies.
Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's should be used as recommended. Sometimes, Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's may have common side effects like nausea, stomach upset, and rash. These side effects do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. However, you are advised to talk to your doctor if you experience these side effects persistently.
Do not take Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's if you're allergic to any ingredient in it. Consult your doctor before using the Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Do not use Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's in more than recommended doses or longer duration as it may cause adverse effects. Avoiding alcohol is recommended to rule out any possibility of side effects.
Uses of Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's
Directions for Use
Key Benefits
Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's is used to treat nutritional deficiencies. It contains Alpha lipoic acid, Folic acid, Pyridoxine, Thiamine, and Mecobalamin. Alpha-lipoic acid is an antioxidant that prevents cell damage and restores vitamin levels in the body. It also protects the nerve cells from damaging degradation products and free radicals. Folic acid is the synthetic form of folate, a water-soluble Vitamin B. It helps in the formation of red blood cells and prevents DNA changes that may lead to cancer. Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) is a water-soluble vitamin that treats and prevents vitamin B6 deficiency, anaemia, peripheral neuropathy, and seizures (fits). It is involved in protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism, the creation of red blood cells and neurotransmitters. Thiamine helps generate energy for the body from nutrients and aids in the growth and development of body cells. Mecobalamin is a coenzyme form of vitamin B12. It regulates body functions, such as cell multiplication, blood formation, and protein synthesis.
Storage
Drug Warnings
Inform your doctor if you have malabsorption syndrome (difficulty absorbing nutrition from food). This disease may make it hard to absorb B complex vitamins when given orally. Your doctor may recommend other dosage forms in such a case. Let your doctor know if you have any blood disorders like pernicious anaemia before starting Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before taking Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's. Excessive alcohol consumption reduces absorption and increases the elimination of folic acid. Hence, please avoid alcohol while using Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's. Keep Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's away from direct sunlight. Do not store Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's above 25ºC.
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Try Vitamin B complex food sources like milk, cheese, eggs, liver and kidney, chicken, red meat, tuna, mackerel, salmon, shellfish, oysters, clams, dark green vegetables such as spinach and kale, beets, avocados, potatoes, whole grains, cereals, kidney beans, black beans, and chickpea.
- Try folate-rich food sources like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, leafy green vegetables, cabbage, kale, spring greens, spinach, peas, chickpeas, kidney beans, and breakfast cereals fortified with folic acid.
- Sprinkle sunflower seeds over your food, vegetables, and salads.
- Include fruits like citrus, banana, and watermelon in your diet.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Avoid excess fatty foods.
Side Effects of Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's
- Nausea
- Stomach upset
- Rash
Habit Forming
Therapeutic Class
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
Mylamin Capsule 10's
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
₹70
(₹6.3 per unit)
53% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockMecodar-Forte Capsule 10's
Ceedar Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
₹119
(₹10.71 per unit)
21% CHEAPERRX
Out of StockRejunerve Plus Capsule 10's
Midas Health Care
₹129
(₹11.61 per unit)
14% CHEAPER
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
FAQs
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List
- ALTRETAMINE
- CISPLATIN
- ARSENIC TRIOXIDE
- PHENYTOIN
- PHENOBARBITAL
- PRIMIDONE
- CHLORAMPHENICOL
- LEVODOPA
- FLUOROURACIL
- TRIMETHOPRIM
- SULFASALAZINE
- CHOLESTYRAMINE
Special Advise
- Clinical monitoring of folic acid, vitamins B1, B12, and B6 levels through blood examinations is recommended.
- Let your doctor and the laboratory staff know if you are using Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's since Pyridoxine may interfere with laboratory tests like urine tests for urobilinogen.
Disease/Condition Glossary
Folate deficiency: Folate deficiency occurs when your body won't have enough folate in your diet. Symptoms include fatigue, grey hair, mouth sores, tongue swelling, and growth problems. Folate deficiency leads to anaemia.
Vitamin B1 deficiency: When the body lacks adequate Thiamine or vitamin B1 levels, it leads to Vitamin B1 deficiency. It commonly leads to beriberi diseases. Symptoms include loss of appetite, weakness, pain in the limbs, shortness of breath, and swollen feet or legs.
Vitamin B6 deficiency: This disease is developed when your body doesn't have adequate levels of a water-soluble vitamin called Pyridoxine or Vitamin B6. Vitamin B6 deficiency symptoms include fatigue, skin rashes, cracked and sore lips, weak immune system, tiredness, tingling in hands and feet, fits and low energy levels.
Vitamin B12 deficiency (cobalamin deficiency): When your body doesn't have adequate mineral levels called Vitamin B12, it leads to Vitamin B12 deficiency. Symptoms include fatigue, breathlessness, numbness, poor balance, and memory trouble.

Have a query?
Alcohol
Safe if prescribed
Excessive alcohol consumption reduces the absorption and increases the elimination of folic acid. Hence, please avoid alcohol while using Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's.
Pregnancy
Consult your doctor
Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's should be used during pregnancy only when advised by your doctor. Let your doctor know if you are pregnant or planning to conceive before taking Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's.
Breast Feeding
Consult your doctor
Pyridoxine and Folic acid in Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's are excreted into the breast milk. Please consult your doctor before taking Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's if you are a breastfeeding mother.
Driving
Safe if prescribed
It is not known if Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's affects your ability to drive. Do not drive or operate machinery if you are not mentally alert and focused.
Liver
Consult your doctor
Let your doctor know if you have any history of liver diseases before taking Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's. Your dosage may be adjusted in case of liver impairment.
Kidney
Consult your doctor
Let your doctor know if you have any history of kidney diseases before taking Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's. Your dosage may be adjusted in case of renal impairment.
Children
Safe if prescribed
The doctor will recommend the dosage of Nuroguard-Plus Capsule 10's based on the child's age and weight.