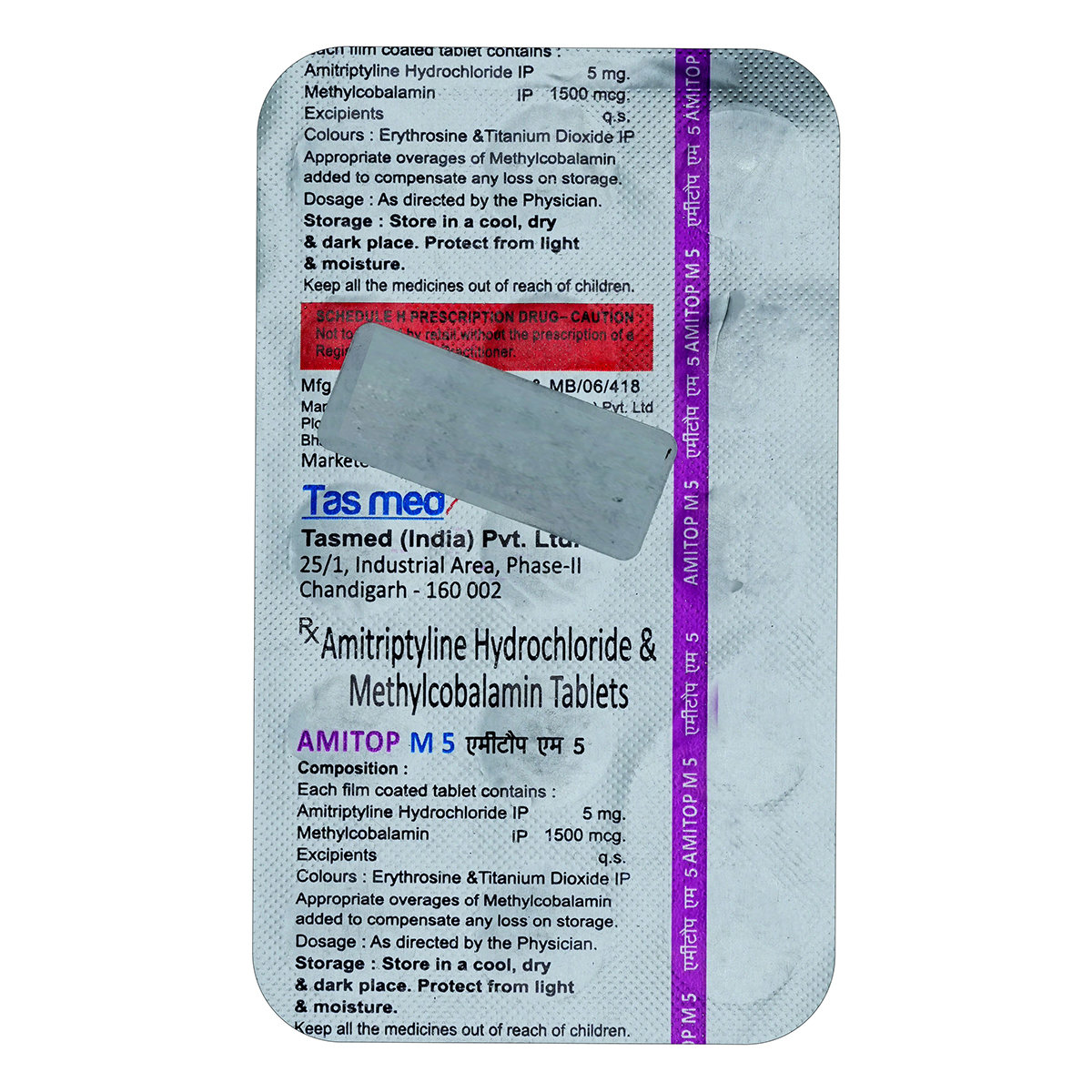
Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin
About Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin
Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin belongs to a group of medications known as central nervous system agents used to manage neuropathic pain due to damaged nerves. Neuropathic pain is pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system. The pain could be intermittent or continuous, like a prickling, stabbing, tingling, or burning sensation.
Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin is a combination of two drugs: Amitriptyline and Methylcobalamin. Amitriptyline belongs to a class of medications known as tricyclic antidepressants, and it works by boosting serotonin levels in the brain. This can make you feel better. This can also alter how your nerves receive pain signals, causing pain to subside. Methylcobalamin is a vitamin B derivative that promotes the synthesis of myelin, which protects nerve fibres and rejuvenates injured nerve cells. They work together to alleviate neuropathic pain (pain from damaged nerves).
Take Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin as prescribed by your doctor. Depending on your medical condition, you are advised to take Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin for as long as your doctor has prescribed it for you. In some cases, you may experience certain common side effects such as constipation, dizziness, dry mouth, feeling sleepy, difficulty peeing, and headache. Most of these side effects do not require medical attention and will resolve gradually over time. However, you are advised to talk to your doctor if you experience these side effects persistently.
Please do not take Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin if you have had an allergic reaction to Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin or any ingredients in it. Tell your doctor if you're pregnant, trying to get pregnant, or breastfeeding. Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin is generally not recommended in pregnancy and breastfeeding. Your doctor will only prescribe Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin for your pain while you're pregnant or breastfeeding if the benefits of taking medicine outweigh the risks. Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin may cause side effects like Light-headedness or dizziness, which may affect your concentration ability. Hence, it is recommended not to drive or operate machinery until you are mentally alert. Seek medical attention if the symptoms persist longer. Avoid consuming alcohol along with Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin as it could lead to increased dizziness and sleepiness. Keep your doctor informed about your health condition and medicines to rule out any side effects.
Uses of Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin
Medicinal Benefits
Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin is a combination of two drugs: Amitriptyline and Methylcobalamin. Amitriptyline belongs to a class of medications known as tricyclic antidepressants. Antidepressants are considered to function by boosting serotonin levels in the brain, making you feel better. And also, these can alter how your nerves receive pain signals, causing pain to subside. Methylcobalamin is a vitamin B derivative that promotes the synthesis of myelin, which protects nerve fibres and rejuvenates injured nerve cells. They work together to alleviate neuropathic pain (pain from damaged nerves).
Directions for Use
Storage
Side Effects of Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin
- Constipation
- Dizziness
- Dry Mouth
- Feeling Sleepy
- Difficulty Peeing
- Headache
- Appetite changes
Drug Warnings
Do not take Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin if you have allergic reactions to Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin or any ingredients. Tell your doctor if you're pregnant, trying to get pregnant, or breastfeeding. Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin is generally not recommended in pregnancy and breastfeeding. Your doctor will only prescribe Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin for your pain while pregnant or breastfeeding if the benefits of taking medicine outweigh the risks. Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin may cause side effects like Light-headedness or dizziness, affecting your concentration. Hence, it is recommended not to drive or operate machinery until you are mentally alert. Seek medical attention if the symptoms persist longer. Avoid consuming alcohol with Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin as it could lead to increased dizziness and sleepiness. Keep your doctor informed about your health condition and medicines to rule out any side effects. Let your doctor know if you have a history of heart disease, severe kidney disease, a blood disorder called porphyria, epilepsy, glaucoma, or suicidal tendency.
Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug interactions: Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin may interact with opioid-based medicines (e.g. codeine, morphine or oxycodone), anti-cancer medicines (e.g. arsenic trioxide), antibiotic medicines (chloramphenicol), and some antidepressant medicines, including herbal remedies (e.g. St John's wort).
Drug-Food Interactions: Avoid consuming alcohol with Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin as it could lead to increased dizziness and sleepiness.
Drug-Disease Interactions: People affected with heart disease, severe kidney disease, a blood disorder called porphyria, epilepsy, glaucoma, and suicidal tendency should consult the doctor before taking the Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin.
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List:
Safety Advice

Alcohol
cautionIt is unclear whether alcohol can be taken while using this medication. However, as a precautionary measure, it is best to avoid alcohol while taking medication.

Pregnancy
cautionAmitriptyline+methylcobalamin is generally not recommended in pregnancy. Your doctor will only prescribe Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin for your pain while you're pregnant if the benefits of taking medicine outweigh the risks.

Breast Feeding
cautionAmitriptyline+methylcobalamin is generally not recommended in breastfeeding. Your doctor will only prescribe Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin for your pain while you're breastfeeding if the benefits of taking medicine outweigh the risks.

Driving
cautionAmitriptyline+methylcobalamin may cause side effects like Light-headedness or dizziness, affecting your ability to concentrate and drive. Hence, it is recommended not to drive or operate machinery until you are mentally alert. Seek medical attention if the symptoms persist longer.

Liver
cautionLimited information was available for the use of Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin in patients with liver impairment. Please consult the doctor. Your doctor will prescribe only if the benefits outweigh the risks.

Kidney
cautionLimited information was available for the use of Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin in patients with Kidney impairment. Please consult the doctor. Your doctor will prescribe only if the benefits outweigh the risks.

Children
cautionLimited information was available for the use of Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin in paediatric patients. Please consult the doctor. Your doctor will prescribe only if the benefits outweigh the risks.
Habit Forming
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Nutritional deficits can cause neuropathy symptoms. Choose foods high in nutrients, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Replace fatty protein sources with lean alternatives and consume modest quantities of healthy fat sources for improved well-being. Saturated fat in fatty meats and dairy products has been linked to inflammation and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Elevated blood sugar levels are linked to various chronic health problems, including diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Increase Omega–3 fatty acids, Fiber, and Antioxidants such as flaxseeds, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and beans to help you maintain a healthy blood sugar level and control your diabetes.
- Create a diet that includes vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, omega-3-rich foods, and lean protein sources.
- Instead of saturated and trans fats, choose monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (fish, nuts, and vegetable oils).
- Select/prepare foods and beverages with fewer added sugars/caloric sweeteners.
- Be mindful of salt; consume no more than 2,300 mg each day.
- Limit or avoid alcohol consumption.
Special Advise
To avoid many illnesses, including peripheral neuropathy, a good diet is typically the first line of defence. The best way to avoid peripheral neuropathy is to monitor any medical condition that puts you at risk closely. Controlling your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes or speaking with your doctor about safe and effective therapies if you suspect you have an alcohol problem. Eat a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein whether you have a medical problem or not.
Patients Concern
Disease/Condition Glossary
Neuropathic pain: Neuropathic pain is pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system. The pain could be intermittent or continuous, like a prickling, stabbing, tingling, or burning sensation.
FAQs
Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin is a combination of two drugs: Amitriptyline and Methylcobalamin. Amitriptyline belongs to a class of medications known as tricyclic antidepressants. Antidepressants are considered to function by boosting serotonin levels in the brain, making you feel better. And also, these can alter how your nerves receive pain signals, causing pain to subside. Methylcobalamin is a vitamin B derivative that promotes myelin synthesis, a material that protects nerve fibres and rejuvenates injured nerve cells. They work together to alleviate neuropathic pain (pain from damaged nerves).
No, it is a prescribed drug given by a physician to prevent specific medical conditions. Taking it on your own can cause unwanted side effects.
Do not discontinue Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin without consulting your doctor, as it could lead to withdrawal symptoms. To treat your condition effectually, continue taking Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin for as long as prescribed. Do not be reluctant to speak with your doctor if you feel any difficulty while taking Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin; your doctor will reduce the dose gradually.
Amitriptyline+methylcobalamin is safe if used in the dose and duration recommended by your doctor. Take it precisely as directed, and do not skip any dose. Follow your doctor's guidelines carefully and inform your doctor if any of the side effects disturb you.
A lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system causes neuropathic pain.
Amitriptyline can alter your appetite. Some people feel hungrier while taking it, while others report feeling less hungry. As a result, your weight may fluctuate when you initially begin taking it.
Most other medicines prescribed for your disease are safe to take with amitriptyline, but some may interact with it. Always consult with your doctor or healthcare expert to ensure that any new medicine you are taking is compatible with amitriptyline.